Jordan policymakers walk tightrope
4 June 2024

Few countries will envy Jordan right now, as one of the Israel-Palestine-adjacent countries most severely impacted both economically and politically by the inevitable spillover of the war in Gaza.
Economic growth in Jordan has inevitably been hit by the conflict, especially in the country’s trade and tourism sectors. Domestic opposition to the war has meanwhile left Ammann walking a tightrope – opposing Israel while remaining part of a broad regional Western-backed coalition that saw Jordan play its part in stemming missile attacks launched by Iran at Israel in April.
The Gaza war is only one of a number of pitfalls confronting the government, which currently faces an unemployment rate of about 22%, desperate water scarcity, and the presence of 1.3 million Syrian refugees topping up the country’s existing population of refugees from Iraq, Palestine and elsewhere.
In these invidious circumstances, the country has performed well, but has also suffered negative consequences.
“Jordan has preserved economic and political stability despite significant external shocks, including social instability in the region (Arab Spring) and wars in neighbouring countries (Iraq and Syria), but these shocks have led to lower growth and significant government debt build-up,” says Erich Arispe, a senior director in Fitch Ratings’ sovereigns group.
For now, Jordan appears to be carrying off the delicate diplomatic work in relation to Israel. It is playing a critical role in the aid effort to Gaza, distancing itself from its neighbour by withdrawing its ambassador from Tel Aviv, and mothballing a planned water-for-energy project.
But it has so far resisted pressure from domestic protesters to adopt a more assertive stance towards Israel – not least since the government is wary of putting its relationship with the US under stress and threatening the $1.45bn in annual aid it receives from Washington.
Jordan’s reliance on Israeli water supplies will also play a part in Amman’s calculus. The kingdom typically sources around 80% of its natural gas from Israel’s offshore Leviathan field.
Despite deep antipathy to Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s government, the reality is that Jordan is locked into a cooperative relationship with its neighbour, including through the Hashemite dynasty’s custodianship of the Al-Aqsa mosque compound in Jerusalem.
Economic effects
While Jordan is unlikely to take radical steps to change its relationship with its neighbour, it remains deeply impacted by Israel’s actions, with the economic implications of the conflict in Gaza being felt nationwide.
The Jordan Hotel Association reported that about half of its hotel reservations were cancelled in October 2023. Fitch Ratings expects that lower tourism inflows, weaker external demand and continued regional political uncertainty will slow growth to 2.3% in 2024, from 2.6% in 2023.
“Nevertheless, we expect that the decline in US and European tourists will be partly compensated by resilience in Jordanian expats and regional tourists. Before the start of the Gaza conflict, Jordanian expats and Arab and GCC tourists accounted for almost three-quarters of total visitors,” says Arispe.
Although the IMF warned in May that the continuation of the war and the trade route disruptions in the Red Sea are affecting sentiment, trade and tourism, barring a significant escalation, the Jordanian economy should be able to navigate the challenges.
While Jordan is primed to run a large current account deficit, at a projected 6.4% of GDP in 2024, this is still lower than the 6.8% deficit recorded in 2023.
According to Fitch, the general government deficit will ease to 2.6% in 2024 and 2.4% in 2025, as expenditure restraint will balance lower-than-budgeted revenue growth and higher interest payments.
“One of the main economic challenges for policymakers is to lift growth prospects to support a sustainable reduction in government debt,” says Arispe.
In its May rating affirmation, Fitch estimated that general government debt (consolidating central government debt holdings of the Social Security Investment Fund and including the Water Authority of Jordan debt and NEPCO guaranteed debt) rose to 93.3% of GDP at the end of 2023.
Although it forecast debt will decline to 91.3% by 2025, this will remain significantly above the projected 53.6% median for sovereigns rated ‘BB’.
“Jordan’s fiscal strategy aims to lower debt to 80% of GDP by 2028 based on a combination of revenue increases, through measures directed at broadening the tax base, and expenditure restraint,” says Arispe.
“Nevertheless, Fitch considers that the sustainability of the current fiscal strategy will depend on the success of reforms aimed at lifting growth prospects combined with increased employment.”
External support
For all the Hashemite kingdom’s vulnerability to regional conflicts, its strategic position also carries advantages. Jordan has attracted substantial external support in the past year, drawing on its status as a regional source of stability.
Early in 2024, the IMF began a new four-year, $1.2bn Extended Fund Facility (EFF).
“From a broader perspective, one of Jordan’s strengths in terms of creditworthiness is the strong relations with multilateral organisations and allies, including the US and partners in the region, which supports Jordan’s financing flexibility. The sovereign is projected to receive total foreign assistance of $3.5bn (6.5% of projected GDP) in 2024,” says Arispe.
In addition, Jordan is attracting significant Gulf investment. In late May, the country’s Investment Ministry announced that Abu Dhabi Development Holding Company (ADQ) had completed the establishment of an infrastructure investment fund company in Jordan. This deal was first mooted during King Abdullah’s visit to Abu Dhabi in 2023.
This company will invest in infrastructure and development projects worth $5bn.
The government also remains committed to its reform agenda, for example, by gradually increasing water utility tariffs last year.
“We expect, though, that the pace of reform progress will continue to depend on the objective of preserving social stability, the resistance of vested interests and institutional capacity constraints,” says Arispe.
Reducing high unemployment is a government priority, especially among women and younger people.
The government is moving ahead with the first phase of its ambitious Economic Modernisation Vision 2023-33, which aims to increase growth potential (5%) and create 1 million jobs over the next decade through higher private investment in strategic sectors.
“The authorities have made progress in terms of digitisation of government procedures, most notably those related to investment, and public administration reform,” says Arispe.
“Nevertheless, increased geopolitical risks make it harder for the government to achieve the 2025 targets under the Vision’s 2023-25 first phase, including reaching 3% growth and exports reaching $13.7bn.”
Above all, the government will hope that external events will not yet have a negative bearing on an ambitious political reform programme that is invariably contingent on favourable regional relations.
Exclusive from Meed
-
 Qatar takes a quantum leap in fulfilling LNG ambitions
Qatar takes a quantum leap in fulfilling LNG ambitions26 February 2026
-
 Contractor appointed for UAE-Saudi power grid interconnection
Contractor appointed for UAE-Saudi power grid interconnection26 February 2026
-
 Egypt’s crisis mode gives way to cautious revival
Egypt’s crisis mode gives way to cautious revival26 February 2026
-
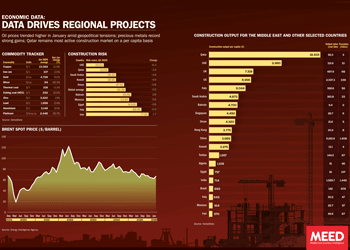 February 2026: Data drives regional projects
February 2026: Data drives regional projects26 February 2026
-
 Lessons learnt from a power plant decommissioning
Lessons learnt from a power plant decommissioning26 February 2026
All of this is only 1% of what MEED.com has to offer
Subscribe now and unlock all the 153,671 articles on MEED.com
- All the latest news, data, and market intelligence across MENA at your fingerprints
- First-hand updates and inside information on projects, clients and competitors that matter to you
- 20 years' archive of information, data, and news for you to access at your convenience
- Strategize to succeed and minimise risks with timely analysis of current and future market trends

Related Articles
-
 Qatar takes a quantum leap in fulfilling LNG ambitions
Qatar takes a quantum leap in fulfilling LNG ambitions26 February 2026
 Commentary
Commentary
Indrajit Sen
Oil & gas editorThe pace at which QatarEnergy has progressed from the front-end engineering and design (feed) stage to the engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) stage of its North Field West liquefied natural gas (LNG) project is impressive.
The state energy company awarded the main EPC contract for North Field West – covering two LNG processing trains with a total capacity of 16 million tonnes a year (t/y) – to a joint venture comprising France’s Technip Energies, Greece/Lebanon-based Consolidated Contractors Company (CCC) and Gulf Asia Contracting (GAC) on 25 February.
The EPC contract, estimated to be worth $8bn, was awarded just one month after QatarEnergy granted the project’s feed contract to Japan-based Chiyoda Corporation.
Such a short interval between the feed and EPC phases for a project as large as North Field West LNG would typically be considered improbable. Industry sources suggest QatarEnergy may have been in discussions with Chiyoda and the Technip Energies–CCC consortium for at least a year regarding the feed and EPC contracts, respectively – particularly given the two-year gap between the project’s announcement in February 2024 and the start of the EPC phase.
Chiyoda, Technip Energies and CCC are also involved in the first two phases of QatarEnergy’s $40bn North Field LNG expansion project. A consortium of Chiyoda and Technip Energies is executing EPC works on the North Field East project, which involves the construction of four LNG trains with a combined capacity of 32 million t/y, following the award of a $13bn contract in February 2021. Meanwhile, a Technip Energies–CCC consortium is carrying out EPC works on two 7.8 million t/y LNG trains as part of the North Field South project, having secured a $10bn contract in May 2023.
More significant, however, is the speed with which QatarEnergy is advancing its strategic objective of reaching a total LNG production capacity of 142 million t/y by the end of the decade.
With all three phases of the North Field LNG expansion programme now under EPC execution – and North Field East scheduled for commissioning later this year – QatarEnergy appears firmly on track to become one of the world’s largest LNG suppliers over the long term, reinforcing Qatar’s economic future in the process.
https://image.digitalinsightresearch.in/uploads/NewsArticle/15781900/main.jpg -
 Contractor appointed for UAE-Saudi power grid interconnection
Contractor appointed for UAE-Saudi power grid interconnection26 February 2026

The GCC Interconnection Authority (GCCIA) has awarded a contract to Omexom, part of France's Vinci Group, for a 400kV overhead transmission line between the UAE and Saudi Arabia.
The $230m project involves the construction of a 96-kilometre, double-circuit 400kV overhead line linking the Al-Silaa substation in Abu Dhabi with the Salwa substation in Saudi Arabia.
The project also includes expanding three key substations in Gonan, Al-Silaa and Salwa and installing upgraded 400kV switchgear, circuit breakers and reactors.
As MEED previously reported, the project is being financed by the Abu Dhabi Fund for Development (ADFD), which signed a $205m financing agreement with GCCIA last July.
France’s EDF is acting as the main consultant on the project.
The award marks Omexom’s first major contract in the region.
The interconnection is intended to strengthen power grid connectivity between the UAE and Saudi Arabia.
It forms part of wider GCC grid expansion plans, including the $700m Oman power grid interconnection, which began implementation earlier this month.
This project marks one of the largest expansions in the authority’s history and involves building a 400kV double-circuit transmission line extending about 530km between the two countries.
https://image.digitalinsightresearch.in/uploads/NewsArticle/15781729/main.jpg -
 Egypt’s crisis mode gives way to cautious revival
Egypt’s crisis mode gives way to cautious revival26 February 2026
 Commentary
Commentary
John Bambridge
Analysis editorIn the past three years, Egypt has faced pressures that would test any market, with collapsed staple revenues, currency volatility and escalating debt pushing it to the fiscal brink. Yet if 2023 and 2024 were years of crisis management, 2025 was a year of economic policy and geopolitical realignment.
Egypt’s foreign policy has always been rooted in pragmatism, but mounting economic fragility has sharpened that instinct. In 2022, Cairo faced just one geopolitical fracas on its borders: Libya. Since 2023 – amid the emergence of conflicts in Sudan and Israel-Palestine – the Egyptian government has become the unwilling inheritor of instability along all three of its land borders. This has eaten into regional trade and Egypt’s stake in it.
In response, Cairo has retrenched around a few simple principles: insulating the domestic economy from geopolitical shocks, preserving internal stability, and leveraging Egypt’s strategic location and role in the region’s security architecture to pursue a more transactional foreign policy. This is inseparable from Egypt’s quest to restore macroeconomic credibility after successive devaluations and inflationary pressure. External actors, meanwhile, see Egypt as too vital a regional lynchpin to fail; US-based funds and Gulf governments have moved quickly to help stabilise Cairo’s finances.
Looking ahead, Egypt’s stated ambition is to move back towards a more routine, predictable monetary policy framework by 2027, with an inflation target of 7% by Q4 2026. This is as much about signalling as substance, but so far investors appear to be buying it. The oil and gas sector is showing renewed momentum, supported by upstream incentives and improved payment discipline towards international operators. Utility infrastructure contracts, meanwhile, reached a decade-high $5bn in 2025, dominated by renewable energy schemes. The water sector is also full of potential, with projects worth about $4.5bn at the prequalification or bid stage.
Beyond energy and utilities, coastal real estate is re-emerging as a hotspot, driven by huge new masterplans across the Mediterranean and Red Sea, supported by public and private entities in the UAE, Saudi Arabia and Qatar. These foreign-backed schemes offer a welcome counterweight to the slowdown in domestically financed projects and are a boon for a construction market that has otherwise cooled.
Egypt remains highly fiscally vulnerable. However, if Cairo can maintain disciplined economic management and continue to use foreign policy pragmatism to secure investment and financial support from its neighbours and the international community, it may yet convert today’s fiscal strain into the foundation for a genuinely investable future.

MEED’s March 2026 report on Egypt includes:
> GOVERNMENT: Egypt adapts its foreign policy approach
> ECONOMY & BANKING: Egypt nears return to economic stability
> OIL & GAS: Egypt’s oil and gas sector shows bright spots
> POWER & WATER: Egypt utility contracts hit $5bn decade peak
> CONSTRUCTION: Coastal destinations are a boon to Egyptian constructionTo see previous issues of MEED Business Review, please click herehttps://image.digitalinsightresearch.in/uploads/NewsArticle/15717634/main.gif -
 February 2026: Data drives regional projects
February 2026: Data drives regional projects26 February 2026
Click here to download the PDF
Includes: Commodity tracker | Construction risk | Brent Spot Price | Construction output
MEED’s March 2026 report on Egypt includes:
> COMMENT: Crisis gives way to cautious revival
> GOVERNMENT: Egypt adapts its foreign policy approach
> ECONOMY & BANKING: Egypt nears return to economic stability
> OIL & GAS: Egypt’s oil and gas sector shows bright spots
> POWER & WATER: Egypt utility contracts hit $5bn decade peak
> CONSTRUCTION: Coastal destinations are a boon to Egyptian constructionTo see previous issues of MEED Business Review, please click herehttps://image.digitalinsightresearch.in/uploads/NewsArticle/15781010/main.gif -
 Lessons learnt from a power plant decommissioning
Lessons learnt from a power plant decommissioning26 February 2026

Al-Kamil power plant, a 280MW, gas-fired power plant in the Sharqiya region of Oman, was recently decommissioned following nearly 20 years of operations as the country’s second independent power plant.
The plant reached commercial operation in 2002, at which time it started to supply electricity to Nama Power & Water Procurement Company under a 15-year power purchase agreement that was later extended to the end of 2021. No further extension was granted so, in 2022, the decommissioning process was initiated.
Al-Kamil power plant was one of the first privately owned power plants in Oman to be decommissioned. The entire process took significantly longer than planned – three years compared to an initial target of 12 months. This was not unexpected, however, as there were not yet any standard processes to follow. Everything was being done for the first time, and proper procedures had to be established.
Starting decommissioning
The decommissioning of a power plant is a complex process and can take as much time to complete as it takes to build a plant. It involves environmental considerations, health and safety protocols, detailed surveys, de-energisation, dismantling, demolition, waste management and the segregation and storage of secondary valuables.
 Careful planning and management are essential to ensure that decommissioning is accomplished safely, cost-effectively and in accordance with all government environmental standards.
Careful planning and management are essential to ensure that decommissioning is accomplished safely, cost-effectively and in accordance with all government environmental standards.Consulting on the decommissioning of Al-Kamil were Dubai’s Golden Sands Marketing Consulting (GSMC), appointed in 2021, alongside Abu Dhabi’s Sustainable Water & Power Company (SWPC) and Dubai’s Tractebel Engineering Company (TEC).
One of the first steps that GSMC undertook was to prepare a master plan covering the entire decommissioning process (see right).
A site investigation was undertaken by GSMC and SWPC early in the process to determine the condition of the power assets and the overall site.
The Al-Kamil power plant was found to have been well maintained, with no major health, safety, security and environment (HSSE) issues.
SWPC prepared the dismantling guidelines covering all plant equipment, and these were reviewed by TEC. The guidelines covered three main phases: the shut down and isolation of all assets; the de-
energisation process; and the dismantling of the plant equipment, its removal from site and the demolition of all remaining civil works.GSMC designed a sales strategy for the plant equipment, taking into consideration the secondary market for power-related equipment, as well as the scrap market in Oman. A competitive procurement process was also followed in an effort to maximise sales revenues from plant equipment.
A separate tender was issued to appoint a demolition contractor to remove the remaining civil works, and once this work was complete, a local environmental engineering company undertook a final environmental report to demonstrate that the site was properly cleared and ready for handover to the original owner, the Housing & Urban Planning Ministry.
Final results
The decommissioning project went well in terms of HSSE considerations, with no fatalities, no lost-time injuries and no first aid injuries over the more than 243,000 total workhours at the site.
There were no material environmental spills or incidents to report, and all above- and below-ground structures were demolished and safely removed from the site in accordance with local requirements.
The final environmental report, completed just before handover, showed that the site was effectively in the same condition as it was when originally taken over at the start of construction.
The decommissioning was also successful from a financial perspective, as revenues from the sale of plant equipment and diesel fuel were beyond what was required to cover the costs associated with the decommissioning process.
Lessons learnt
Many lessons were learnt during the process that can benefit future power plant decommissioning efforts in the region.
> Notify key stakeholders early: Key stakeholders are those that have a vested interest in the project, either through ownership of certain assets on site, such as grid connection assets, or via regulation, such as the environmental authority. Many of these stakeholders take time to respond, so notifying key stakeholders early in the process can ensure that unnecessary delays are avoided.
> Prioritise HSSE: For any future decommissioning project, HSSE must be a top priority, and this should be the focus throughout the entire decommissioning process – at all levels of work and management.
The site manager at Al-Kamil installed a 24/7 closed-circuit television camera, which proved to be extremely effective in terms of monitoring progress and identifying potential HSSE issues before they became an incident. This simple and cost-effective practice should be replicated for all future decommissioning projects.
> Appoint the environmental consultant early in the process: It is advisable to appoint an environmental consultant early in the process. The consultant is needed to coordinate activities with the local environmental authority and obtain a no-objection letter or certificate, complete an environmental management report and an update of the environmental impact assessment, which includes an environmental baseline.
Ideally, these reports and environmental authority approvals should be completed well before any work is under way at the site. This information is also useful to potential bidders for the sale of equipment, or to contractors involved in the dismantling and demolition process.
> Submit an environmental management plan for approval: It is unlikely that any environmental authority will provide a no-objection letter or certificate without reviewing the environmental plan. It is therefore necessary to complete the plan early, prior to informing the environmental authority. This can minimise potential delays in starting the decommissioning process.
As a general practice, an environmental consultant should be brought on board early in the process, ideally once the overall master plan is approved by the company.
> Establish a proactive steering committee: This was done at Al-Kamil and proved to be effective when it came to overseeing project progress and dealing with issues as they arose. Certain members of the steering committee visited the site regularly and undertook spot HSSE inspections.
At Al-Kamil, the overall decommissioning was relatively straightforward as the plant was in a remote area. However, decommissioning a power plant in a busier location, or when part of the power plant remains in operation, is more challenging. Under these circumstances, a steering committee is vital.
> Set realistic delivery and completion timelines: Decommissioning a power plant is a complex process. The initial timeline to complete the process for Al-Kamil was one year, which was the best estimate at the time as there were no benchmarks or references in Oman. However, the actual completion time turned out to be three years – longer than the approximately 2.5 years it took to build the plant, from the start of construction in early 2001 to full commercial operation in July 2003.
Realistic delivery dates should be set for contractors, suppliers and others involved in the decommissioning process. This is likely to result in better pricing, as bidders tend to factor in higher contingencies with shorter or fast-track delivery dates. More realistic delivery dates also help management to allocate staff resources and manage the decommissioning budget.
Finally, realistic delivery dates help to manage owner and shareholder expectations regarding project completion.
Given the experience with Al-Kamil, a reasonable decommissioning timeline for a power plant is probably close to the actual construction timeline for the plant involved.
> Allow time to maximise revenues from the sale of assets: The market value for Al-Kamil’s power assets was estimated at a value significantly higher than the prevailing scrap value. This was based in part on the value of similar gas turbine units, after adjusting for age, usage and other factors that affect the net market value. However, the company realised a much lower value, even after retendering the equipment sales in an effort to get a better price.
It appears that prices close to the market rate are only achievable if there is time to find a suitable buyer. This can take many months or even years – typically a longer time than the owners of power plants wish to take.
Moreover, as renewables continue to penetrate the market, there is less worldwide demand for used gas turbine units. Prevailing market supply and demand conditions also have a bearing on the sale price for secondary equipment, and this factor needs to be considered.
If time is of the essence, then power plant owners need to accept the fact that the expected revenues will likely be on the low side, although still higher than the scrap value of the assets.
Main image: Picture 1: Al-Kamil power plant as constructed; Picture 2: Post decommissioning
https://image.digitalinsightresearch.in/uploads/NewsArticle/15780944/main.gif


